Contents¶
VideoIngestion Module¶
The VideoIngestion (VI) module ingests the video frames from video sources in the Open Edge Insights for Industrial (Open EII) stack for processing. The example of video sources include video files or cameras such as Basler, RTSP, or USB cameras. The VI module can also perform video analytics, when it runs with the classifier and post-processing user defined functions (UDFs).
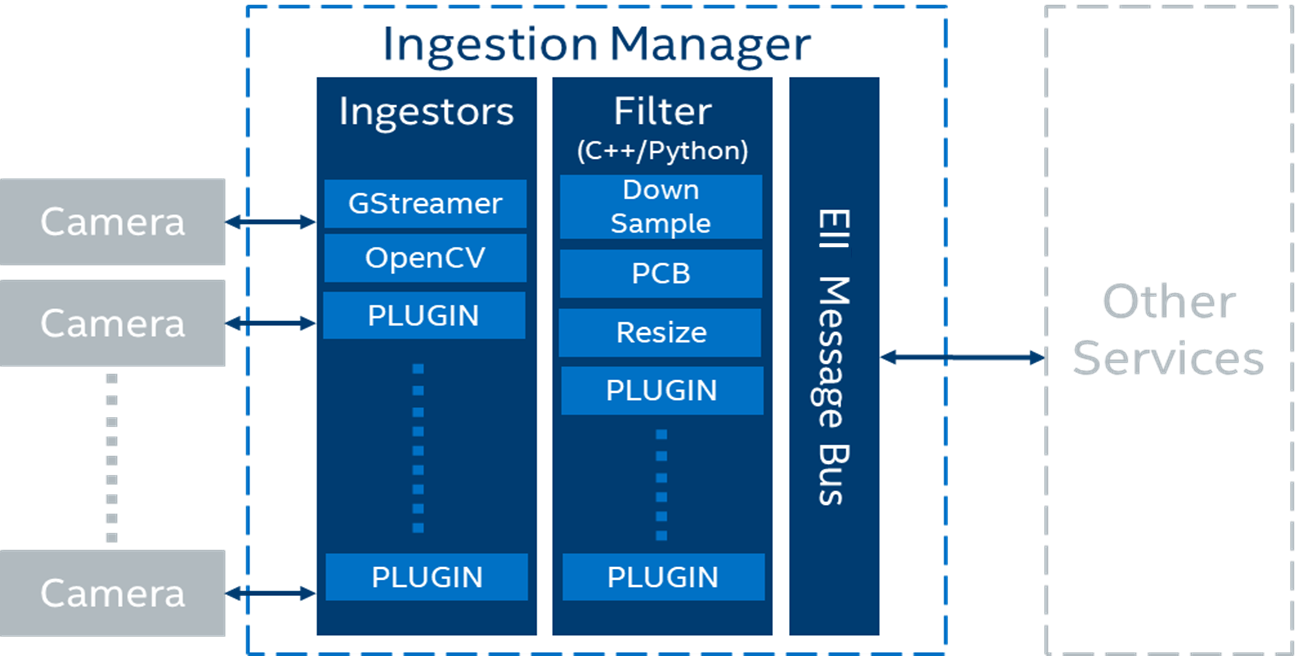
The high-level logical flow of the VideoIngestion pipeline is as follows:
The app reads the application configuration via the Configuration Manager which has details of the
ingestor,encoding, andUDFs.Based on the ingestor configuration, the app reads the video frames from a video file or camera.
[
Optional] The read frames are passed to one or more chained native or python UDFs for doing any pre-processing. Passing through UDFs is optional and it is not required to perform any pre-processing on the ingested frames. With chaining of UDFs supported, you also have classifier UDFs and any post-processing UDFs like resize etc., configured in theudfskey to get the classified results. For more details, refer to the ../common/video/udfs/README.md.App gets the msgbus endpoint configuration from system environment. Based on the configuration, the app publishes data on the mentioned topic on the MessageBus.
Note
The following use cases are suitable for a single node deployment, where the overhead of the VideoAnalytics (VA) service can be avoided:
The VA service is not required, when the VI service is configured with a UDF that does the classification. The VI service uses multiple UDFs for pre-processing, classification, and post-processing.
The VA service is not required, when the VI service uses the Gstreamer Video Analytics (GVA) elements. Pre-processing, classification, and post-processing (using the vappi gstreamer elements) can be done in the gstreamer pipeline. If required, you can configure post-processing by having multiple UDFs in the VI service.
Configuration¶
For configuration details refer to the following topics:
MessageBus configuration respectively.
JSON schema(
[WORK_DIR]/IEdgeInsights/VideoIngestion/schema.json)
All the app module configurations are added to the distributed key-value store under the AppName env, as mentioned in the environment section of the app’s service definition in the docker-compose. If the AppName is VideoIngestion, then the app’s config is taken from the /VideoIngestion/config key via the Open EII Configuration Manager.
Note
The Developer mode-related overrides go in the
docker-compose-dev.override.ymlfile.For the
jpegencoding type,levelis the quality from0 to 100. A higher value means better quality.For the
pngencoding type,levelis the compression level from0 to 9. A higher value means a smaller size and longer compression time.Use the JSON validator tool for validating the app configuration for the schema.
Ingestor Config¶
Open EII supports the following type of ingestors:
For more information on the Intel RealSense SDK, refer to librealsense.
VideoIngestion Features¶
Refer the following to learn more about the VideoIngestion features and supported camera:
Image Ingestion¶
The Image ingestion feature is responsible for ingesting the images coming from a directory into the Open EII stack for further processing. The OpenCV Ingestor supports image ingestion.
Image ingestion supports the following image formats:
Jpg
Jpeg
Jpe
Bmp
Png
Refer the following snippet for configuring the config.json([WORK_DIR]/IEdgeInsights/VideoIngestion/config.json) file for enabling the image ingestion feature.
OpenCV Ingestor
{ // "ingestor": { "type": "opencv", "pipeline": "/app/img_dir/", "poll_interval": 2, "loop_video": true, "image_ingestion": true }, "sw_trigger": { "init_state": "running" }, "max_workers":1, // }
The description of the keys used in the config.json file is as follows:
pipeline — Provides the path to the images directory that is volume mounted.
poll_interval — Refers to the pull rate of image in seconds. Configure the
poll_intervalvalue as required.loop_video — Would loop through the images directory.
image_ingestion — Optional boolean key. It is required to enable the image ingestion feature.
Note:
The image_ingestion key in the
config.jsonneeds to be set true for enabling the image ingestion feature.Set the
max_workersvalue to 1 as"max_workers":1in theconfig.jsonfiles for VideoIngestion/config.json([WORK_DIR]/IEdgeInsights/VideoIngestion/config.json) and VideoAnalytics/config.json([WORK_DIR]/IEdgeInsights/VideoAnalytics/config.json). This is to ensure that the images sequence is maintained. If themax_workersis set more than 1, then more likely the images would be out of order due to those many multiple threads operating asynchronously.If the resolution of the image is greater than
1920×1200, then the image will be resized towidth = 1920andheight = 1200. The image is resized to reduce the loading time of the image in the Web Visualizer and the native Visualizer.
Volume mount the image directory present on the host system. To do this, provide the absolute path of the images directory in the docker-compose file.
Refer the following snippet of the ia_video_ingestion service to add the required changes in the docker-compose.yml([WORK_DIR]/IEdgeInsights/VideoIngestion/docker-compose.yml) file. After making the changes, ensure that the builder.py([WORK_DIR]/IEdgeInsights/build/builder.py) is executed before you build and run the services.
ia_video_ingestion:
...
volume:
- "vol_eii_socket:${SOCKET_DIR}"
- "/var/tmp:/var/tmp"
# Add volume
# Please provide the absolute path to the images directory present in the host system for volume mounting the directory. Eg: -"home/directory_1/images_directory:/app/img_dir"
- "<path_to_images_directory>:/app/img_dir"
...
UDF Configurations¶
Ensure that you are using the appropriate UDF configuration for all the video and camera streams. If the UDF is not compatible with the video source, then you may not get the expected output in the Visualizer or the Web Visualizer screen. Use the dummy UDF, if you are not sure about the compatibility of the UDF and a video source. The dummy UDF will not do any analytics on the video, and it will not filter any of the video frames. You will see the video streamed by the camera, as it is displayed on the video output screen in the Visualizer or Web Visualizer.
Refer the following configuration for the
dummyUDF:
"udfs": [{
"name": "dummy",
"type": "python"
}]
>
Apply the same changes in the VideoAnalytics configuration if it is subscribing to VideoIngestion.
Updating Security Context of VideoIngestion Helm Charts¶
Complete the following steps to update Helm charts to enable K8s environment to access or detect Basler Camera, USB devices, and NCS2 Devices:
#. Open the EII_HOME_DIR/IEdgeInsights/VideoIngestion/helm/templates/video-ingestion.yaml file
#.
Update the following security context snippet
securityContext: privileged: truein the yaml file as:
... ... ... imagePullPolicy: {{ $global.Values.imagePullPolicy }} securityContext: privileged: true volumeMounts: - name: dev mountPath: /dev ...
Rerun the
builder.pyto apply these changes to your deployment Helm charts.
Camera Configurations¶
The camera configurations for the VI module are as follows:
For a video file:
OpenCV Ingestor
{ "type": "opencv", "pipeline": "./test_videos/pcb_d2000.avi", "poll_interval": 0.2 "loop_video": true }
Gstreamer Ingestor
{ "type": "gstreamer", "pipeline": "multifilesrc loop=TRUE stop-index=0 location=./test_videos/pcb_d2000.avi ! h264parse ! decodebin ! videoconvert ! video/x-raw,format=BGR ! appsink" }
For more information or configuration details for the multifilesrc element, refer to the docs/multifilesrc_doc.md.
GenICam GigE or USB3 Cameras¶
For more information or configuration details for the GenICam GigE or the USB3 camera support, refer to the GenICam GigE/USB3.0 Camera Support.
Prerequisites for Working with the GenICam Compliant Cameras¶
The following are the prerequisites for working with the GeniCam compliant cameras.
Note
For other cameras such as RealSense, RSTP, and USB (v4l2 driver compliant) revert the changes that are mentioned in this section. Refer to the following snip of the ia_video_ingestion service, to add the required changes in the docker-compose.yml([WORK_DIR]/IEdgeInsights/VideoIngestion/docker-compose.yml) file of the respective ingestion service (including custom UDF services). After making the changes, before you build and run the services, ensure to run the builder.py([WORK_DIR]/IEdgeInsights/build/builder.py).
For GenICam GigE cameras:
ia_video_ingestion:
# Add root user
user: root
# Add network mode host
network_mode: host
# Please make sure that the above commands are not added under the environment section and also take care about the indentations in the compose file.
...
environment:
...
# Add HOST_IP to no_proxy and ETCD_HOST
no_proxy: "${RTSP_CAMERA_IP},<HOST_IP>"
ETCD_HOST: "<HOST_IP>"
...
# Comment networks section as below as it will throw an error when network mode host is used.
# networks:
# - eii
# Comment ports section as below
# ports:
# - 64013:64013
For GenIcam USB3.0 cameras:
ia_video_ingestion:
# Add root user
user: root
...
environment:
# Refer [GenICam GigE/USB3.0 Camera Support](/3.0.1/IEdgeInsights/VideoIngestion/docs/generic_plugin_doc.html) to install the respective camera SDK
# Setting GENICAM value to the respective camera/GenTL producer which needs to be used
GENICAM: "<CAMERA/GenTL>"
...
Note
If the GenICam cameras do not get initialized during the runtime, then on the host system, run the
docker system prunecommand. After that, remove the GenICam specific semaphore files from the/dev/shm/path of the host system. Thedocker system prunecommand will remove all the stopped containers, networks that are not used (by at least one container), any dangling images, and build cache which could prevent the plugin from accessing the device.If you get the
Feature not writablemessage while working with the GenICam cameras, then reset the device using the camera software or using the reset property of the Generic Plugin. For more information, refer the README.In the
IPCmode, if the Ingestion service is running with therootprivilege, then theia_video_analyticsandia_visualizerservice subscribing to it must also run with therootprivileges.In a multi-node scenario, replace
in “no_proxy” with the leader node’s IP address. In the TCP mode of communication, the msgbus subscribers and clients of VideoIngestion are required to configure the
Endpointin theconfig.jsonfile with the host IP and port under theSubscribersorClientsinterfaces section.
Gstreamer Ingestor
GenICam GigE/USB3.0 cameras
{ "type": "gstreamer", "pipeline": "gencamsrc serial=<DEVICE_SERIAL_NUMBER> pixel-format=<PIXEL_FORMAT> exposure-time=5000 exposure-mode=timed exposure-auto=off throughput-limit=300000000 ! videoconvert ! video/x-raw,format=BGR ! appsink" }
Note:
Generic Plugin can work only with GenICam compliant cameras and only with gstreamer ingestor.
The above gstreamer pipeline was tested with Basler and IDS GigE cameras.
If
serialis not provided then the first connected camera in the device list will be used.If
pixel-formatis not provided then the defaultmono8pixel format will be used.If
widthandheightproperies are not set then gencamsrc plugin will set the maximum resolution supported by the camera.By default
exposure-autoproperty is set to on. If the camera is not placed under sufficient light then with auto exposure,exposure-timecan be set to very large value which will increase the time taken to grab frame. This can lead toNo frame received error. Hence it is recommended to manually set exposure as in the below sample pipline when the camera is not placed under good lighting conditions.throughput-limitis the bandwidth limit for streaming out data from the camera(in bytes per second).
Hardware trigger based ingestion with Gstreamer ingestor
{ "type": "gstreamer", "pipeline": "gencamsrc serial=<DEVICE_SERIAL_NUMBER> pixel-format=<PIXEL_FORMAT> trigger-selector=FrameStart trigger-source=Line1 trigger-activation=RisingEdge hw-trigger-timeout=100 acquisition-mode=singleframe exposure-time=5000 exposure-mode=timed exposure-auto=off throughput-limit=300000000 ! videoconvert ! video/x-raw,format=BGR ! appsink" }
Note:
For PCB use case, use the
widthandheightproperties of gencamsrc to set the resolution to1920x1200and make sure it is pointing to the rotating PCB boards, as seen in thepcb_d2000.avivideo file for the PCB filter to work.
Refer the following example pipeline:
{ "type": "gstreamer", "pipeline": "gencamsrc serial=<DEVICE_SERIAL_NUMBER> pixel-format=ycbcr422_8 width=1920 height=1200 exposure-time=5000 exposure-mode=timed exposure-auto=off throughput-limit=300000000 ! videoconvert ! video/x-raw,format=BGR ! appsink" }
Refer to the docs/basler_doc.md for more information/configuration on Basler camera.
RTSP Cameras¶
Refer to the docs/rtsp_doc.md for information/configuration on RTSP camera.**
OpenCV Ingestor
{ "type": "opencv", "pipeline": "rtsp://<USERNAME>:<PASSWORD>@<RTSP_CAMERA_IP>:<PORT>/<FEED>" }
Note: OpenCV for RTSP will use software decoders.
Gstreamer Ingestor
{ "type": "gstreamer", "pipeline": "rtspsrc location=\"rtsp://<USERNAME>:<PASSWORD>@<RTSP_CAMERA_IP>:<PORT>/<FEED>\" latency=100 ! rtph264depay ! h264parse ! vaapih264dec ! vaapipostproc format=bgrx ! videoconvert ! video/x-raw,format=BGR ! appsink" }
Note: The RTSP URI of the physical camera depends on how it is configured using the camera software. You can use VLC Network Stream to verify the RTSP URI to confirm the RTSP source.
For RTSP simulated camera using cvlc
OpenCV Ingestor
{ "type": "opencv", "pipeline": "rtsp://<SOURCE_IP>:<PORT>/<FEED>" }
Gstreamer Ingestor
{ "type": "gstreamer", "pipeline": "rtspsrc location=\"rtsp://<SOURCE_IP>:<PORT>/<FEED>\" latency=100 ! rtph264depay ! h264parse ! vaapih264dec ! vaapipostproc format=bgrx ! videoconvert ! video/x-raw,format=BGR ! appsink" } **Refer `docs/rtsp_doc.md </3.0.1/IEdgeInsights/VideoIngestion/docs/rtsp_doc.html>`_ for more information/configuration on rtsp simulated camera.**
USB v4l2 Cameras¶
For information or configurations details on the USB cameras, refer to docs/usb_doc.md.
OpenCV Ingestor
{ "type": "opencv", "pipeline": "/dev/<DEVICE_VIDEO_NODE>" }
Gstreamer Ingestor
{ "type": "gstreamer", "pipeline": "v4l2src device=/dev/<DEVICE_VIDEO_NODE> ! video/x-raw,format=YUY2 ! videoconvert ! video/x-raw,format=BGR ! appsink" }
RealSense Depth Cameras¶
RealSense Ingestor"ingestor": { "type": "realsense", "serial": "<DEVICE_SERIAL_NUMBER>", "framerate": <FRAMERATE>, "imu_on": true },
Note
RealSense Ingestor was tested with the Intel RealSense Depth Camera D435i.
RealSense Ingestor does not support poll_interval. If required, use framerate to reduce the ingestion frames per second (FPS).
If the
serialconfig is not provided then the first RealSense camera in the device list will be connected.If the
framerateconfig is not provided then the default framerate of30will be applied. Ensure that the framerate provided is compatible with both the color and depth sensor of the RealSense camera. With the D435i camera only framerate 6,15,30, and 60 is supported and tested.The IMU stream will work only if the RealSense camera model supports the IMU feature. The default value for
imu_onis set tofalse.